Abstract
Metabolic reprogramming is recognized as one of the key hallmarks in acquiring aggressive phenotype and chemoresistance in solid tumors and hematologic malignancies.
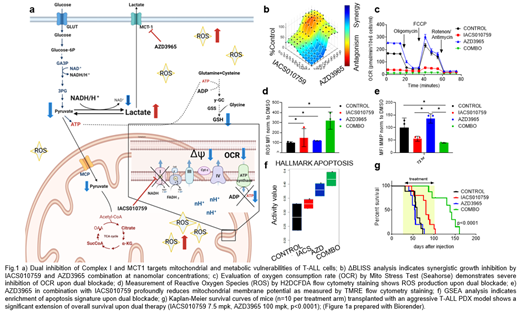
We have previously demonstrated that T-ALL are characterized by significant dependency on oxidative phosphorylation (OxPhos) with ability to utilize glutamine either in oxidative or reductive directions of TCA cycle, when mitochondria are blocked by Complex I Inhibitor (Baran N, et al. ASH 2020). To survive upon Complex I blockade leukemic cells require functional monocarboxylate transporter MCT1, that enables excretion of lactate and permissive pyruvate flux (Fig.1 a).
Here we show that metabolic intervention utilizing OxPhos blockade can be potentiated by targeting MCT1 transporter and propose a novel metabolic synthetic lethality that could be exploited to eradicate T-ALL and other OxPhos-dependent malignancies.
We first demonstrated that Complex I inhibition leads to increased MCT1 expression; on the contrary, MCT1 transporter blockade forces cells to increase OxPhos. In turn, the combinatorial therapy with Complex I inhibitor (IACS-010759) and MCT1 inhibitor (AZD3965) causes loss of ATP content (Fig. 1b), significant reduction of cell number and massive induction of apoptosis. Mechanistically, the combination treatment further reduced oxygen consumption rate (OCR) (Fig. 1c) and increased extracellular acidification rate, as measured by Seahorse. In concert with those results, dual inhibition led to TCA blockade, accumulation of intracellular lactate and depletion of glutamine, cystathionine and glutathione, indicating severe disruption of redox balance as measured by mass spectrometry and confirmed by significant accumulation of intracellular and mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) (Fig. 1d), loss of mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨ) (Fig. 1e) and subsequent mitochondria swelling. RNAseq data showed simultaneous upregulation of glycolysis and glutathione-related processes as possible mechanisms of metabolic compensation, yet strong upregulation of genes regulating apoptosis related to mitochondria dysfunction (Fig. 1f).
Real-time hyperpolarized MRI based metabolic imaging studies with [1-13C]-pyruvate in patient-derived xenografts in vivo revealed significant decrease of lactate-to-pyruvate ratio in mice treated with AZD3965 or IACS-010759 alone, and in mice treated with drug combination. [13C]-Glucose isotope tracing analysis in patient-derived xenografts in vivo revealed an increased intracellular trapping of lactate as a marker of treatment effectiveness in mice subjected to dual blockade.
While MCT1 inhibition induced only moderate reduction of leukemia growth in vitro and tumor burden in vivo, combination with IACS-010759 depleted significantly both, circulating and marrow/spleen/liver resident leukemia cells. Mechanistically, inhibition of MCT1 by AZD3965 therapy in leukemia-bearing mice led to lactate accumulation, OCR increase, moderate ROS production and mitochondrial membrane hyperpolarization, while Complex I blockade resulted in upregulation of MCT-1, reduction of OCR, lactate production and increase of ROS ; consequently, combinatorial therapy caused complete mitochondria shut-down and drastic inhibition of tumor growth both in vitro and in vivo in two xenografts models and led to significant extension of overall survival (p<0.0001) (Fig. 1g). In summary, these results demonstrate a novel synthetic vulnerability of concomitant blockade of OxPhos and MCT-1, uncovering metabolic checkpoints that can ultimately translate into successful therapies in T-ALL and OxPhos-dependent malignancies.
Skwarska: Halilovich E, Wang Y, Morris E, Konopleva M, Skwarska A.: Patents & Royalties: Combination of a MCL-1 inhibitor and midostaurin, uses and pharmaceutical composition thereof.. Konopleva: Reata Pharmaceuticals: Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company, Patents & Royalties: intellectual property rights; Rafael Pharmaceuticals: Other: grant support, Research Funding; Stemline Therapeutics: Research Funding; Eli Lilly: Patents & Royalties: intellectual property rights, Research Funding; Ascentage: Other: grant support, Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: grant support, Research Funding; Ablynx: Other: grant support, Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Other: grant support, Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Grant Support, Research Funding; Novartis: Other: research funding pending, Patents & Royalties: intellectual property rights; Cellectis: Other: grant support; Sanofi: Other: grant support, Research Funding; KisoJi: Research Funding; Calithera: Other: grant support, Research Funding; Forty Seven: Other: grant support, Research Funding; Agios: Other: grant support, Research Funding; F. Hoffmann-La Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: grant support.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal